A Cybereason report shows that 49% of enterprises who pay the ransom either get only part of their data back, or none at all
JOHANNESBURG, South Africa, October 21, 2022/APO Group/ —
By Ning Yun, Director of Data Storage Department of Huawei SAR (Huawei.com)
Ransomware is striking at an alarming rate. Information technology research and consultancy company Gartner predicts, by 2025, at least 75% of IT organizations will face one or more attacks. Refined hacking tools and extortion strategies have made ransomware the biggest threat to individual, enterprise, and national data security.
Constant ransomware attacks cause huge damage
When ransomware strikes, it steals and encrypts valuable data. Encrypted data can be decrypted only by paying the hackers a ransom. Hackers, working through darknets, usually demand Bitcoin to make the payment as difficult as possible to trace. The damage ransomware creates is great, as are hackers’ profits.
According to leading investment consulting firm Cybersecurity Ventures, by 2031, ransomware is expected to attack a business, consumer, or device every 2 seconds. In 2021, this number was only 11 seconds. Even at that lower frequency, that same year, global ransomware damages reached US$20 billion — 61 times more than in 2015 (US$325 million). The largest ransom — so far — was US$70 million. But do ransoms solve the problem? No. A Cybereason report shows that 49% of enterprises who pay the ransom either get only part of their data back, or none at all. 80% of enterprises who pay the ransom are targeted a second time. Ransoms are also not the only problem: ransomware damages brands, causes long service interruptions, exposes enterprises to legal liability, and more. Such collateral damage can be enormous: as much as 23 times the ransom.
- In March 2021, hackers encrypted 15,000 devices belonging to an insurance corporation. Vast numbers of customer data files were at risk of being leaked. The company paid US$40 million to retrieve the data.
- In May 2021, ransomware halted all the operations of an oil pipeline giant for 11 days. Gasoline prices in the country rose to their highest level in seven years, leading to panic buying. The company paid a ransom of US$4.4 million.
- In April 2022, a leading car manufacturer had to cut its annual production by 500,000 vehicles following an attack on its suppliers which resulted in a 1.4 TB data leak.
- In May 2022, two attack waves caused a country to declare a cyber security emergency. They damaged basic services like healthcare, and even international trade.
There are many more examples. Hackers target large, high-value enterprises and industries. Government, energy, transportation, finance, manufacturing, and healthcare are their main objectives, but no one is safe.
Ransomware trends to know
Ransomware is extremely good at disguise. It has many ways to get into your system, for example storage, phishing emails, Trojans, social networks, and malicious insiders. It is difficult to detect and defend against. A typical attack encrypts or deletes all local data copies and can even target disaster recovery (DR) centers, making it impossible to quickly restore data. What follows, according to a ZDNet report, is an average of 16 business days system downtime. The average cost to recover from an attack, calculated by Sophos, is US$1.85 million.
There are four important ransomware trends:
Hackers focus on large enterprises and infrastructure
Instead of launching broad campaigns, ransomware attacks now increasingly focus on high-value targets. The research that hackers need to do for this approach to work is difficult, time-consuming — weeks or even months! — and expensive, but the potential profits make it worthwhile. Elaborate attacks make even previously well protected organizations potential victims, and also threaten government departments.
- Ransomware as a Service (RaaS)
Rapid development of network and information technologies as well as encrypted digital currencies has created a hotbed for malicious actors. Ransomware operators now sell ransomware-related services to other attackers through customized solutions, memberships, or subscriptions. This lowers the barrier to entry for launching ransomware attacks, resulting in explosive ransomware growth.
Double extortion becoming the new normal
Ransomware is not limited to encrypting data and demanding ransoms. Attackers also steal data, and threaten to leak it. Even if an enterprise has a recent backup, it still cannot risk a leak of confidential information and subsequent public scrutiny and compliance proceedings.
A typical attack encrypts or deletes all local data copies and can even target disaster recovery (DR) centers, making it impossible to quickly restore data
APT-like attack capabilities
Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) refers to a complex continuous network attack customized by expert attackers to take full advantage of a victim’s vulnerabilities. Ransomware attacks, featuring greater and greater precision and planning, are beginning to show a strong resemblance to APT attacks.
Data security needs
Complex ransomware poses a great challenge for many current defense measures. Traditional data security protection focuses on the network (such as the firewall and security gateways) and on hosts to prevent ransomware intrusions and limit spread. This, however, neglects ransomware’s ability to disguise itself and lurk in the system for a long time in order to get access permissions to a large volume of key data. In other words, once the system is infected, traditional data security protection is useless. A better solution is needed.
The Defense-in-Depth framework developed by defense contractor Northrop Grumman provides good ideas on how to move forward and build stronger protection. This approach to cybersecurity features five defensive mechanism layers: perimeter, network, endpoint, application, and data security.
- Perimeter and network security protection, established at the network layer, defends using firewalls, sandboxes, and situation awareness.
- Endpoint and application security protection, established at the host layer, defends using access control, security patches and audits, and antivirus software.
The last layer, data security, is where data storage comes in. In the modern, digital age, data storage needs to do more than just store data. It needs to serve as the last line of defense: protect data with anti-tamper technologies, detect abnormal I/Os generated by ransomware, and prevent data leaks using encryption technologies. In addition to all this, it needs to ensure it is possible to recover clean, uninfected data by keeping data copies in backup storage and in a physically isolated zone.
Building powerful ransomware defense with professional storage
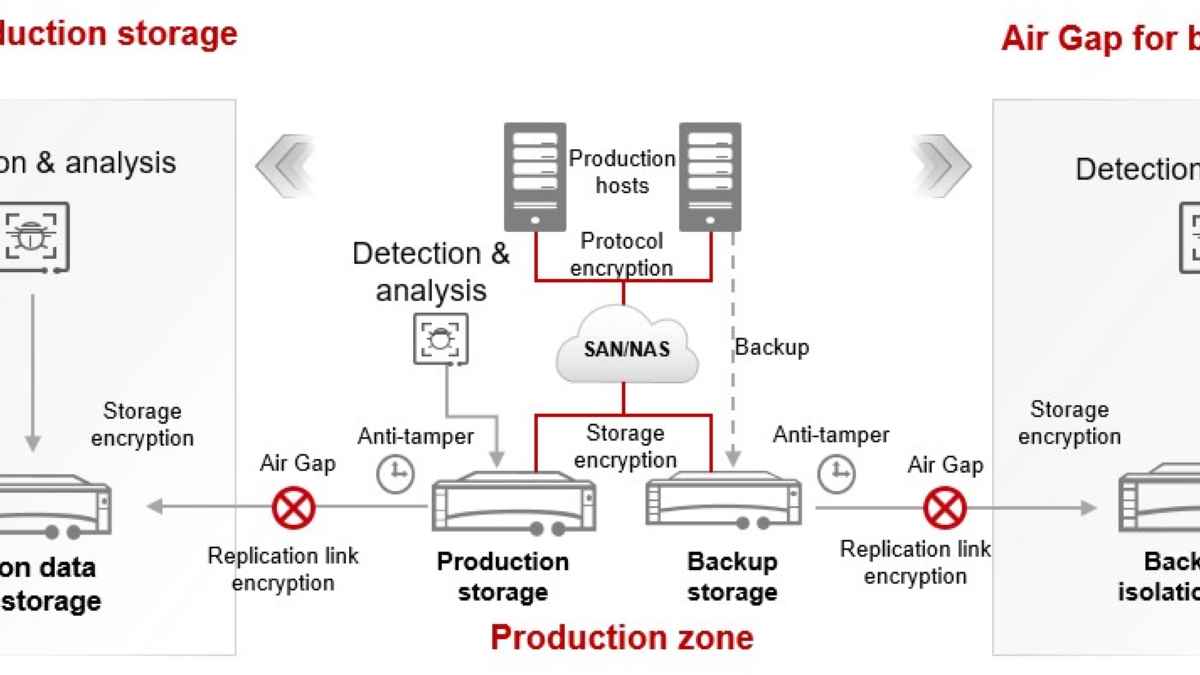
Providing dual protection with production and backup storage, Huawei ransomware protection storage solution uses four key technologies to build a complete solution which prevents viruses from hiding and stealing or tampering with data: ransomware detection, data anti-tampering, air gap replication, and end-to-end data encryption. Let’s take a look at why dual protection and the four key features are so effective:
- Dual ransomware protection with both primary and backup storage
In this solution, both primary and backup (OceanProtect Backup Storage) storage provide all-round ransomware protection features, ensuring the system always has a clean data copy for quick service recovery. OceanProtect Backup Storage also provides an ultra-fast recovery speed: up to 172 TB/hour, five times faster than the benchmark in the industry. This helps enterprises slash service downtime and economic losses.
- Four key technologies for comprehensive protection
Ransomware detection (ransomware has nowhere to hide): Huawei ransomware detection and analysis feature delivers 99.9% accuracy for production and backup storage before, during, and after attacks. Before an attack, the storage works to intercept ransomware before it has a chance to strike. If an attack does still occur, the storage acts quickly to secure the system, working with security devices such as firewalls to isolate hosts that send abnormal I/Os, preventing ransomware from spreading to other hosts. After the attack, the storage examines data copies to ensure they are clean.
Data tampering prevention (data cannot be modified): WORM file system and secure snapshot technology block file tampering. The WORM system supports setting a protection period, preventing modification or deletion of production or backup data for the duration of the period. Read-only secure snapshots provide similar protection: they do not allow deletion or modification of data during a configured protection period.
Physical isolation (clean data copies are physically isolated): Air-gap technology enables storing a clean copy of production and backup storage data in a physically isolated zone. Even if — unlikely though it may be — both production and backup storage are compromised, the isolation zone will have a clean copy that can be used to quickly restore services. Setting the replication Service Level Agreement (SLA) will automatically replicate periodic data copies from the production or backup storage to the isolation environment. Since the replication link is active only during replication, the possibility of ransomware accessing data in the isolation zone is relatively low. For added security, the isolation zone storage also features multi-layer data protection, supporting anti-tamper features such as secure snapshots.
End-to-end encryption (data will not be leaked): Huawei storage ensures zero data leaks on the storage transmission network and storage through encryption of: protocol, production and backup storage, air-gap replication link, and remote replication transmission of data and backup copies. Even if hackers break the storage or intrude the storage network, they have no access to the confidential data thanks to the encryption deployment.
End-to-end encryption (data will not be leaked): Huawei storage uses end-to-end encryption technology to ensure no data leaks either on storage devices or on the storage transmission network. The encryption covers protocol, production and backup data, the air-gap replication link, and remote data replication. Even if hackers manage to enter a system, they will not crack confidential data.
Defending against ransomware
Huawei’s ransomware protection storage solution is working 24/7 around the world for large customers in energy, finance, transportation, manufacturing, and government.
Better safe than sorry. Installing ransomware protection after the fact is too late. A comprehensive ransomware protection storage solution is the best way to stop or mitigate ransomware.
For more information about how you can build powerful defense for your data, visit our website (https://bit.ly/3RRI74g).
Distributed by APO Group on behalf of Huawei Enterprise.

 Business5 days ago
Business5 days ago
 Business3 days ago
Business3 days ago
 Business5 days ago
Business5 days ago
 Business4 days ago
Business4 days ago
 Events4 days ago
Events4 days ago
 Energy4 days ago
Energy4 days ago
 Energy2 days ago
Energy2 days ago
 Events3 days ago
Events3 days ago













